Operators in Python
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values.
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators
- Membership Operators
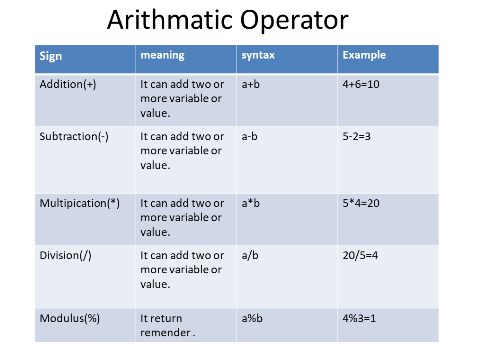
Arithmetic operators
It is used to perform arithmatic operation like Addition,Subtraction,mutiplication,division and modulus.
Types of arithmatic operators is given below:
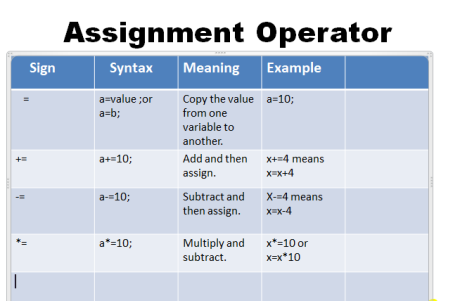
Assignment operators
The word Assignment is stand for 'assign'+'ment' means "assign value to some variable".the value of right side which have same datatype to left side.
Types of assignment operators is given below:
Relational Operators
In relational operators, operators compare the values of two operands. For example, if we have two numbers, x equals 12 and y equals 13, we can use operators like >, <, <=, >=, and ==. If we compare x < y, it returns 1; if x > y, it returns 0. Types of relational operators are given below:

Logical Operators
When we combine two or more Condition and implement original condition then we are use logical operater
Types of Logical operators is given below

Bitwise Operators
In Python programming there are 6 bitwise operators and
types of Bitwise operators and its function are
and(&)
The bitwise AND operator is denoted by single ampersand: &. While performing the bitwise AND operation is 1 if both the bits have the value as 1 otherwise, the result is always 0.
Example
a=7
b=11
print("a & b ",a&b)
Output
11
or(|)
The bitwise OR operator is denoted by: |. While performing the bitwise OR operation is 1 if any one of the bits have the value as 1; otherwise, the result is always 0.
Example
a=7
b=11
print("a|b",a|b)
Output
15
bitwise not(~)
The bitwise NOT operator is denoted by: '~'. While performing the bitwise NOT operation is 1 if bit is 0; otherwise, the result is always 0.
Example
a=7
print("a=",~a)
Output
~7=248
Right shift(>>)
The bitwise Right Shift operator is denoted by: '>';, and when two numbers, right shifts the bits of the first operand, the second operand decides the number of places to shift.
Example
a=7
print(a,">>1=",a>>1)
Output
7>>1=5
Left shift(<<)
The bitwise Left shift operator is denoted by: <, and when two numbers, left shifts the bits of the first operand, the second operand decides the number of places to shift.
Example
a=7
print(a,"<<1=",a<<1)
Output
7<<1=22
Membership Operators
Membership operators are used to check the a sequence is present in an object or not.
